Urgent Info
- There is no Urgent Info now.
GSIC
| Addr. | 2-12-1 O-okayama, Meguroku, Tokyo 152-8550 JAPAN |
| Contact this mail address. |
You are here
Turbulence Simulation using FMM
R. Yokota, L.A.Barba, Boston University, yokota[at]bu.edu, labarba[at]bu.edu
T. Narumi, University of Electro-Communications, narumi[at]cs.uec.ac.jp
K. Yasuoka, Keio University, yasuoka[at]mech.keio.ac.jp
Background and Objectives
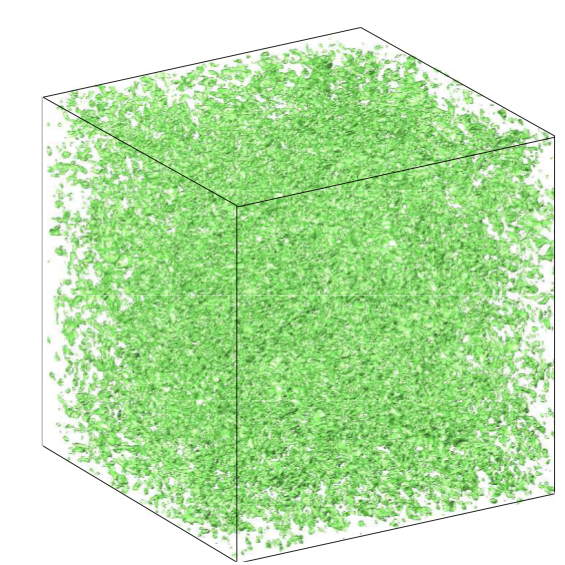
Traditional methods for simulating turbulent flows have been the spectral method (based on FFT) and finite difference method (based on linear solvers). The fast multipole method (FMM) is more parallel compared to these algorithms. Our goal is to take turbulence simulation to the next level of parallelism by making use of our FMM solver.
Description of runs
The simulation of isotropic turbulence for 2048^3 unknowns is performed by an FMM based method and an FFT based method, and the computational efficiency is compared.
Mesh: 2048^3
Re_λ: 500
Library: ExaFMM vs. FFTW
Results
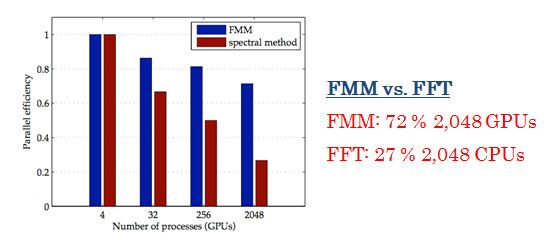
Both the FMM and FFT based solvers take approximately 30 seconds per time step on 2,048 GPUs.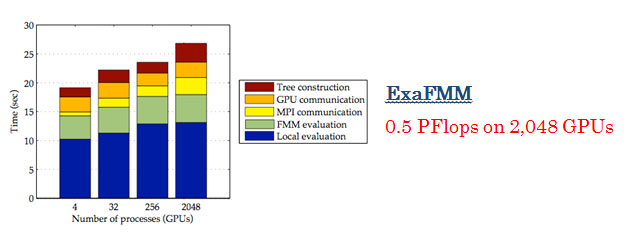
![[GSIC] Tokyo Institute of Technology | Global Scientific Information and Computing Center](../../_img/logo_en.jpg)